Bodegus: A Serious Game Intervention to Shape Informal Business Practices
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17083/rtem4q38Keywords:
Informal business practices, formalization attitude, formalization intention, ethical decision-making, virtue ethics, utilitarianismAbstract
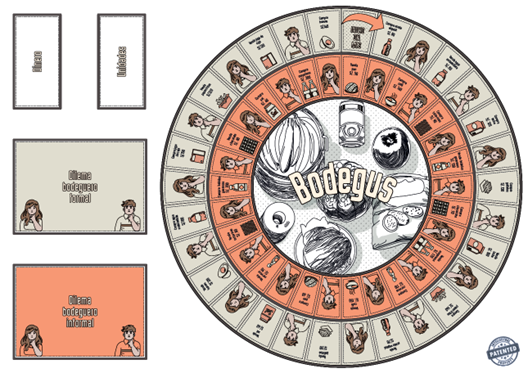
This study aimed to test whether a serious-game intervention (Bodegus) strengthens the relationship between the perceived usefulness of formal business practices and the intention to formalize these practices. Using a pre-experimental pre-test–post-test design, 38 Peruvian entrepreneurs played Bodegus as part of a workshop on formality and completed a questionnaire measuring the constructs’ perceived usefulness and intention to formalize business practices. The constructs were modeled as second-order composites in the areas of governance/leadership, legal/tax, and accounting/finance. The analysis was conducted using a multi-group Structural Equation Model with the partial least-squares method. Although the group-difference tests were not statistically significant, the relationship between the two variables was stronger in the post-test model, showing higher explanatory and predictive metrics; therefore, the results were interpreted as exploratory. The originality of this study lies in presenting and detailing Bodegus as a serious-game intervention study that tests two opposing normative ethical approaches: virtue ethics and utilitarianism. Its impact consists of offering a replicable design and an analytical approach for ethical/behavioural education on informality, guiding course design, and micro-level policy initiatives aimed at fostering formal business practices.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Luis Demetrio Gómez García, Gloria Maria Zambrano Aranda, Emerson Jesus Toledo Concha

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
IJSG copyright information is provided here.