Fibonacci Level Adjustment for Optimizing Player’s Performance and Engagement
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17083/ijsg.v10i2.586Keywords:
Adaptive level adjustment, Computer game, Fibonacci sequence , Skill detectionAbstract
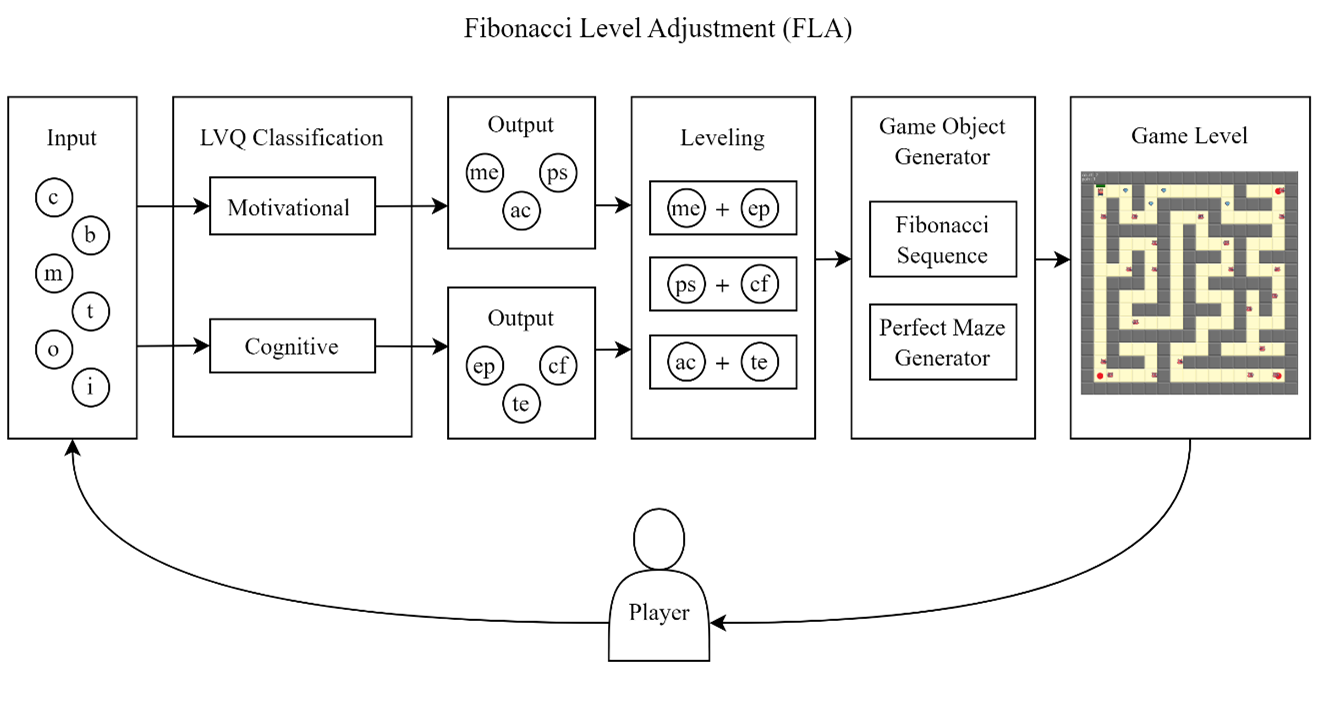
Players’ engagement intensity in computer games is influenced by the level of difficulty the game offers. Traditional game-level plots adopt linear increases that sometimes do not match the users’ skill growth, causing boredom and hampering the users’ further skill growth. In this study, a nonlinear level adjustment scenario was proposed based on the Fibonacci sequence that provides gradual increases in the early stages of the games but more drastic changes in later phases. Here, the game’s difficulty level was automatically decided by a machine learning method. To test the proposed method, comparisons between four level adjustments in computer games: traditional plots, self-selected plots, linear adaptive plots, and the proposed nonlinear adaptive plots were run. The experiment was carried out with 40 testers. The experiment results show that the best player’s peak level in the proposed nonlinear adjustment was twice as high as that of linear adjustment. Also, the number of stages required to reach the peak under the proposed scenario was half that of linear games. This high playing performance goes hand in hand with deep playing engagement. The results demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed level adjustment algorithm.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Faiz Hilmawan Masyfa, Herman Tolle, Tibyani Tibyani, Pitoyo Hartono

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
IJSG copyright information is provided here.